waterfall model
What is the waterfall model?
The waterfall model is a linear, sequential approach to the software development lifecycle (SDLC) that is popular in software engineering and product development.
The waterfall model uses a logical progression of SDLC steps for a project, similar to the direction water flows over the edge of a cliff. It sets distinct endpoints or goals for each phase of development. Those endpoints or goals can't be revisited after their completion.
Dr. Winston W. Royce at the Lockheed Software Technology Center introduced the concept in a paper published in 1970 on his experience developing software for satellites. However, Royce didn't use the term waterfall; instead, he referred to the downstream value of documentation.
The waterfall model continues to be used in industrial design applications. It's often cited as the first software development methodology. The model is also used more generally as a high-level project management methodology for complicated, multifaceted projects.
Who uses the waterfall model?
Project teams and project managers use the waterfall model to achieve goals based on the needs of their business. The model is used in many different project management contexts, such as in construction, manufacturing, IT and software development.
In the waterfall method, each step is dependent on the output of the previous step. There's a linear progression to the way these projects unfold.
For example, in construction, these three general steps are usually followed:
- A building's physical design is created before any construction begins.
- The foundation is poured before the skeleton of a building is erected.
- The skeleton of the building is completed before the walls are built.
On a manufacturing line, steps are followed sequentially in a controlled order when building a product until the finished deliverable is created.
The waterfall model doesn't include a project's end user or client as much as other development methodologies. Users are consulted during the initial stages of gathering and defining requirements, incorporating client feedback after that. By leaving the client out of the main part of the waterfall process, the development team moves quickly through the phases of a project.
This methodology is good for teams and projects that want to develop a project according to fixed or unchanging requirements set forth at the beginning of the project. Waterfall projects have a high degree of process definition with little or no output variability. Waterfall is also a good choice if the project is constrained by cost or time.
Projects based on the waterfall model are well defined, predictable and have specific documentation. They also have the following characteristics:
- fixed requirements;
- ample resources;
- an established timeline;
- well-understood technology; and
- unlikely to require significant changes.
In software development, if an application needs to work on the first try at the risk of losing customers, waterfall is a suitable method because it sets out to achieve that goal. Contrast that with Agile project management and development methodology. Agile methods use ongoing reiteration, which is an iterative approach that involves designing, developing and testing software in repeated cycles that build upon each other.
Phases of the waterfall model
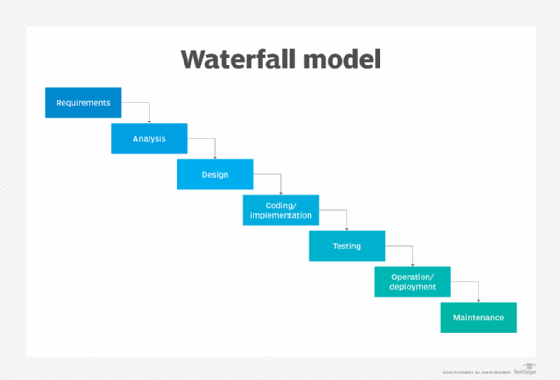
When used for a software development process, the waterfall methodology has seven stages:
- Requirements. Potential requirements, deadlines and guidelines for the project are analyzed and placed into a formal requirements document, also called a functional specification. This stage of development defines and plans the project without mentioning specific processes.
- Analysis. The system specifications are analyzed to generate product models and business logic to guide production. This is also when financial and technical resources are audited for feasibility.
- Design. A design specification document is created to outline technical design requirements, such as the programming language, hardware, data sources, architecture and services.
- Coding and implementation. The source code is developed using the models, logic and requirement specifications designated in the prior phases. Typically, the system is coded in smaller components, or units, before being put together.
- Testing. This is when quality assurance, unit, system and beta tests identify issues that must be resolved. This may cause a forced repeat of the coding stage for debugging. If the system passes integration and testing, the waterfall continues forward.
- Operation and deployment. The product or application is deemed fully functional and is deployed to a live environment.
- Maintenance. Corrective, adaptive and perfective maintenance is carried out indefinitely to improve, update and enhance the product and its functionality. This could include releasing patch updates and new versions.
Before moving to the next phase in the waterfall process, there's usually a review and sign off to ensure all defined goals have been met. For example, developers would ensure each unit of technology is properly integrated in the implementation phase before moving to the testing phase.
Advantages of the waterfall model
Today, Agile methodology is often used in place of the waterfall model. However, there are advantages to the waterfall approach, such as the following:
- enables large or changing teams to move toward a common goal that's been defined in the requirements stage;
- forces structured, disciplined organization;
- simplifies understanding, following and arranging tasks;
- facilitates departmentalization and managerial control based on the schedule or deadlines;
- reinforces good coding habits to define before implementing design and then code;
- enables early system design and specification changes to be easily done; and
- clearly defines milestones and deadlines.
Disadvantages of the waterfall model
Disadvantages of the waterfall model typically center around the risk associated with a lack of revision and flexibility. Specific issues include the following:
- Design isn't adaptive; when a flaw is found, the entire process often needs to start over.
- Method doesn't incorporate midprocess user or client feedback, and makes changes based on results.
- Waterfall model delays testing until the end of the development lifecycle.
- It doesn't consider error correction.
- The methodology doesn't handle requests for changes, scope adjustments and updates well.
- Waterfall doesn't let processes overlap for simultaneous work on different phases, reducing overall efficiency.
- No working product is available until the later stages of the project lifecycle.
- Waterfall isn't ideal for complex, high-risk ongoing projects.
Waterfall model software and tools
Gantt charts are a common management tool for waterfall projects. These charts enable easy visualization of sequential phases, letting project managers map dependencies and subtasks to each phase of the process. They provide a clear view of timelines and deadlines for each phase.
Some project management software products that feature Gantt charts include the following:
- Asana,
- Jira,
- Microsoft Excel,
- Microsoft Project,
- Microsoft SharePoint,
- ProjectManager,
- Smartsheet and
- Wrike.
Project management software often includes other tools to help waterfall-based teams complete their tasks. Some important capabilities to have in project management software are the following:
- team collaboration,
- note taking,
- testing and development, and
- data analytics and visualization.
Alternatives to waterfall
Besides Agile software development methods, alternatives to the waterfall process include the following:
- joint application development,
- rapid application development,
- sync and stabilize, and
- spiral model.
Software development teams today often use Agile and DevOps methodologies instead of the waterfall method. Learn how the three approaches compare.






